type
Post
status
Published
date
Jul 5, 2023
slug
2023/07/05/QEMU-debugging-Linux-kernel-environment-construction
summary
tags
开发
Linux
qemu
category
Linux
created days
new update day
icon
password
Created_time
Jul 5, 2023 09:26 AM
Last edited time
Mar 1, 2025 01:50 AM
0 准备操作
1 编译环境准备
一个最小可运行 Linux 操作系统需要内核镜像 bzImage 和 rootfs ,本文整理了其制作、安装过程,调试命令,以及如何添加共享磁盘。
我的开发环境为 Arch linux,具体的宿主机内核编译环境可以参考下面的文章。
2 内核源码准备
你可以选择直接去 https://www.kernel.org/ 下载压缩包,也可以之间克隆一个。
git clone -b staging-testing git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/gregkh/staging.git
1 配置并编译内核
1 配置内核选项
cd staging # cd linux-6.4.1 make x86_64_defconfig make menuconfig
在配置菜单中,启用内核debug,关闭地址随机化,不然断点处无法停止。
Kernel hacking ---> [*] Kernel debugging Compile-time checks and compiler options ---> Debug information (Rely on the toolchain's implicit default DWARF version) (X) Rely on the toolchain's implicit default DWARF version [*] Provide GDB scripts for kernel debugging Processor type and features ---> [ ] Randomize the address of the kernel image (KASLR)
2 编译内核
开始编译内核,-j 指定并行编译作业数。最终生成
/path/to/your/kernel/code/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage 文件。make -j 12
2 配置 Busybox
启动内核还需要一个具有根文件系统的磁盘镜像文件,根文件系统中提供可供交互的shell程序以及一些常用工具命令。我们借助busybox工具来制作根文件系统。
busybox 官网如下,最近版本为 BusyBox 1.36.1 (stable)
1 下载并解压
tar xvf busybox-1.36.1.tar.bz2 cd busybox-1.36.1
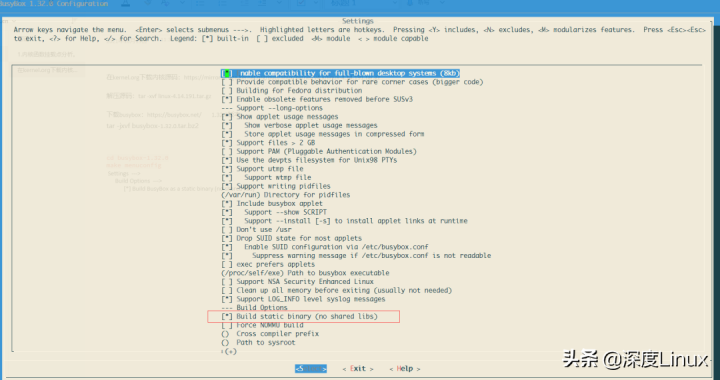
2 把 busybox 配置为静态编译
Settings ---> [*] Build static binary (no shared libs)
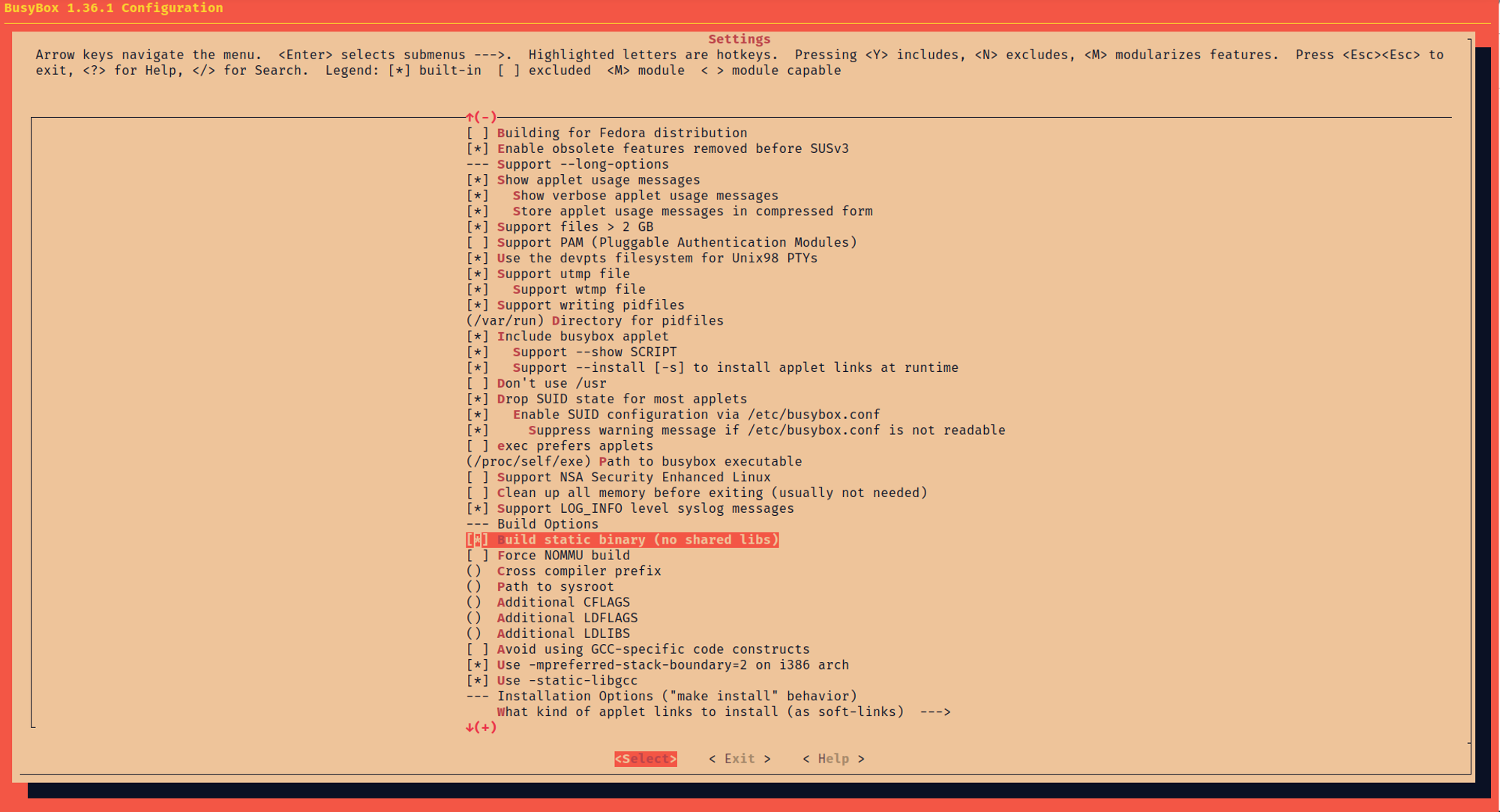
3 编译 busybox
make -j 12
3 制作 rootfs
接下来制作rootfs镜像文件,并把busybox安装到其中。
使用dd命令创建文件,并格式化为ext4文件系统。
dd if=/dev/zero of=rootfs.img bs=1M count=512 mkfs.ext4 rootfs.img
创建用于挂载该镜像文件的目录
rootfs,挂载后才能往里面写入 busybox。使用 mount 命令将
rootfs.img 挂载到 rootfs 目录,编译 busybox 并写入 rootfs 目录中。mkdir rootfs sudo mount -t ext4 -o loop rootfs.img ./rootfs sudo make install CONFIG_PREFIX=./rootfs
对写入的busybox进行补充配置。
cd rootfs/ sudo mkdir proc dev etc home mnt sudo cp -r ../examples/bootfloppy/etc/* etc/
最后,卸载rootfs.img
cd .. sudo umount rootfs
至此,一个带有rootfs的磁盘镜像制作完成。
4 启动qemu
使用如下命令启动无GUI的qemu,参数含义如下:
-kernel # 指定编译好的内核镜像 -hda # 指定硬盘 -append "root=/dev/sda" 指示根文件系统 console=ttyS0 把QEMU的输入输出定向到当前终端上 -nographic 不使用图形输出窗口 -s 是-gdb tcp::1234缩写,监听1234端口,在GDB中可以通过target remote localhost:1234连接
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel ./staging/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage -hda=./disk/rootfs.img -append "root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0" -nographic
启动后如下图:
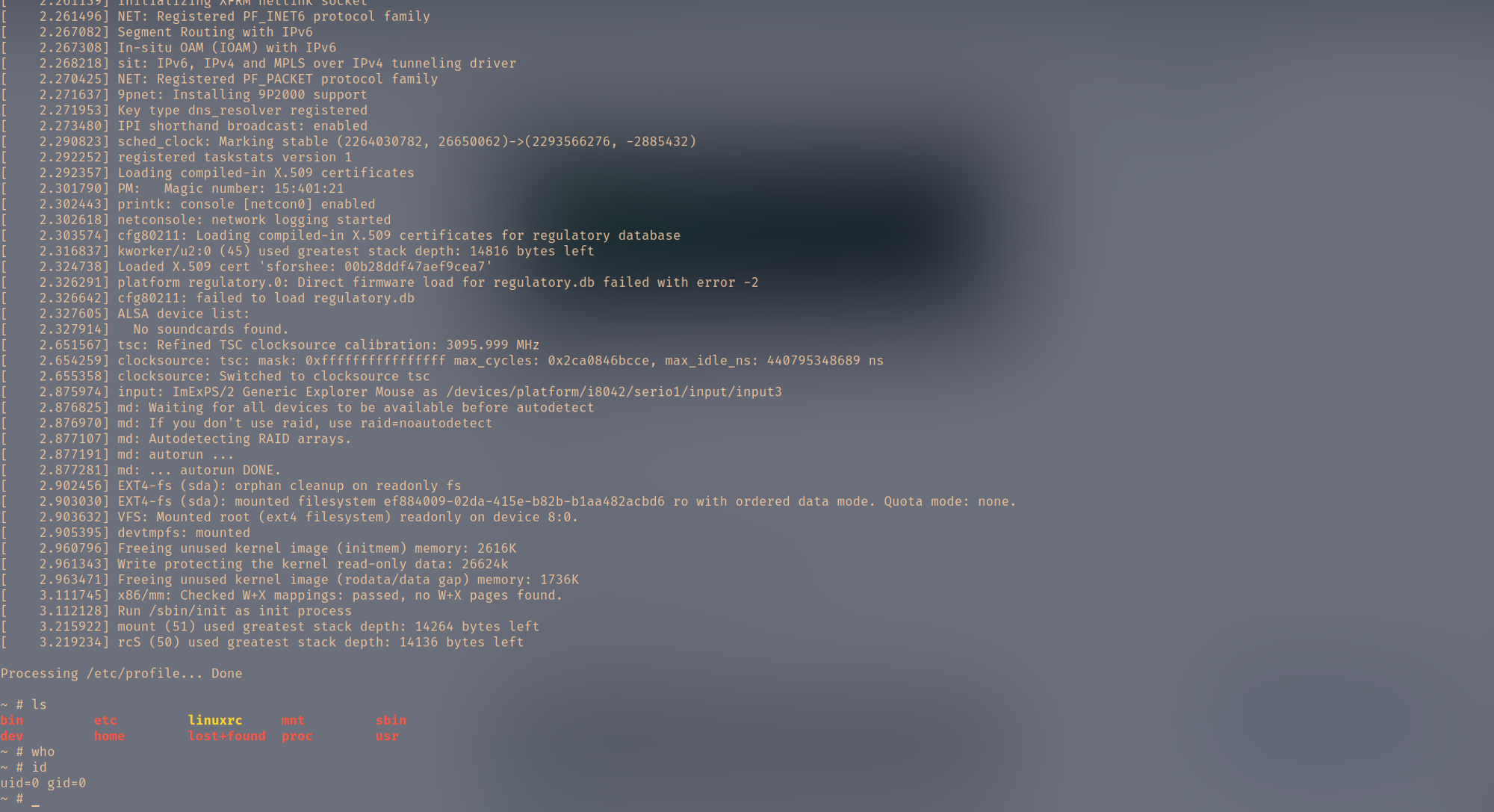
Ctrl+A 松开后按C退出qemu。
5 内核函数调试
启动命令中添加-s参数与-S参数启动qemu。
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel ./staging/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage -hda=./disk/rootfs.img -append "root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0" -s -S -smp 1 -nographic
- 这个时候 qemu 终端会卡住
- 启动 gdb ,开启调试即可
gdb vmlinux (gdb) target remote localhost:1234 Remote debugging using localhost:1234 0x000000000000fff0 in exception_stacks () (gdb) c # qemu 开始运行 Continuing.
至此,完成了qemu环境下使用gdb进行内核函数的调试。
6 添加共享磁盘
有时候需要在宿主机和qemu虚拟机之间共享文件,添加一个共享磁盘将有助于该项工作。
创建64MB磁盘镜像文件,并格式化为ext4,作为共享磁盘备用。
dd if=/dev/zero of=ext4.img bs=512 count=131072 mkfs.ext4 ext4.img
修改qemu启动命令,使用-hdb增加一个磁盘。
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel ./staging/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage -hda=./disk/rootfs.img -append "root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0" -s -S -smp 1 -nographic -hdb ~/shadisk/ext4.img
进入qemu系统后使用mount命令挂载sdb到mnt目录。
在原系统中挂载ext4.img,实现qemu与原系统的文件共享。
sudo mount -t ext4 -o loop ext4.img ./share
至此,可以在宿主机器share目录下,与qemu中的虚拟机器进行文件共享。
7 参考资料
欢迎加入“喵星计算机技术研究院”,原创技术文章第一时间推送。

- 作者:tangcuyu
- 链接:https://expoli.tech/articles/2023/07/05/QEMU-debugging-Linux-kernel-environment-construction
- 声明:本文采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议,转载请注明出处。
相关文章
2023-02-20
[Email] mutt + msmtp + Gmail
2023-07-25
[MIT 6.s081] Lab: Copy-on-Write Fork for xv6 实验记录
2025-07-29
【转载】(一)Linux进程调度器-基础 - LoyenWang - 博客园
2025-03-06
【转载】EtherCAT主站IgH解析(一)--主站初始化、状态机与EtherCAT报文 - 沐多 - 博客园
2025-07-28
【转载】Linux RCU原理剖析(一)-初窥门径 - LoyenWang - 博客园
2025-07-28
【转载】Linux RCU原理剖析(二)-渐入佳境 - LoyenWang - 博客园